Cognitive intelligence is defined as the capability to acquire, process, and understand information in cognitive psychology. It includes several functions, like learning and reasoning.
Although most candidates have skills that help them complete role-specific tasks, it’s harder to measure whether they possess the necessary cognitive intelligence to fully understand and adapt to the complexities of their roles.
In this article, we break this down by answering what cognitive intelligence is, exploring cognitive ability tests you can use to evaluate candidates, and examining the difference between cognitive intelligence and emotional intelligence.
Table of contents
- What is cognitive intelligence?
- Why is cognitive intelligence important at work?
- 7 examples of cognition and intelligence
- Cognitive intelligence vs. emotional intelligence in the workplace
- What types of cognitive tests are there?
- Use cognitive tests during recruitment to make better hiring decisions
- Cognitive intelligence FAQs
What is cognitive intelligence?
Cognitive intelligence is the ability to acquire, process, and understand information and use it to generate new knowledge. It encompasses thinking, senses, and experience and has several intellectual functions, such as paying attention, learning, memory, judgment, and reasoning.
Cognition intelligence or cognitive function are neuroscience terms that translate to the ability of employees to acquire new skills and knowledge and tackle their work tasks successfully in practice. It’s important because today’s job market requires workers to be fast learners proficient in several areas, and this need will only continue to increase.
According to the World Economic Forum, the most important job skills of the future include cognitive skills, such as creativity, problem-solving, innovation, and analytical thinking.
Finding talent with good cognition intelligence is the key to keeping your workforce agile and solution-oriented.
Why is cognitive intelligence important at work?
Cognitive processes are one of the most important predictors of job success. Research suggests it predicts job performance for middle-level complexity jobs with 66% accuracy.
Other research shows that cognitive intelligence is even more important for complex roles, such as managerial positions, predicting job performance with 74% accuracy.
So, why is cognition and intelligence so important at work?
There are several reasons:
Problem-solving skills: Employees who excel at cognitive tasks can better analyze complex situations, respond to stimuli, identify patterns, and create effective solutions
Learning and adaptation: A strong cognitive foundation helps individuals who self-report as excelling in cognitive intelligence process new information, adapt to changes, and learn new skills quickly
Decision-making: Cognitive thinking helps employees evaluate available data to make more informed decisions, which is crucial for strategic planning
Productivity: Better attention and focus help employees work more efficiently, which improves performance
Creativity and innovation: The brain’s ability to think creatively and make connections between seemingly unrelated concepts supports innovation, which is vital for organizational success
Make the right hiring decision
Book a free live demo to learn how you can use our cognitive ability tests to make the right hiring decision.
7 examples of cognition and intelligence
Here are seven examples of cognition and intelligence that show how these traits help employees perform their jobs successfully:
Cognition intelligence | Example |
1. Problem-solving | A manager suddenly learns that a worker isn’t available, so they communicate with the team and delegate tasks to others to meet an incoming deadline. |
2. Critical thinking | A financial analyst evaluates the pros and cons of different investment options to recommend the best portfolio to their client. |
3. Decision-making | Facing budget constraints, a marketing director must choose between two campaign strategies. They weigh the potential ROI and audience reach, selecting the one that best aligns with the company’s goals and budget. |
4. Learning | An English-speaking professional takes a digital analytics course in Spanish to perfect his language skills and better understand consumer behavior and campaign performance. They can optimize their language fluency and future marketing strategies to improve results, thanks to structured learning. |
5. Memory | During a challenging trial, a lawyer recalls specific laws and precedents during a court argument to strengthen their case. |
6. Attention | In a busy warehouse, a supervisor notices a small discrepancy in inventory. They track down errors, prevent significant shipping mistakes, and ensure accurate inventory records. |
7. Creativity | An entrepreneur creates an innovative marketing strategy to launch a new product in a competitive market, capturing consumer interest despite many competitor products. |
Cognitive intelligence vs. emotional intelligence in the workplace
Human intelligence doesn’t only include information processing and mental ability. The human brain possesses multiple types of intelligence, including higher-level working memory and emotional intelligence.
Experts suggest there is a difference between emotional intelligence vs. cognitive intelligence.
Emotional intelligence is the ability to understand and perceive emotions, especially when communicating with others. Strong emotional intelligence helps people manage and express their feelings, recognize others’ emotions, and empathize.
In this sense, cognitive and emotional intelligence are quite different, although both are necessary in the workplace. Research suggests that emotional intelligence is responsible for 58% of job performance success.
Whereas cognitive abilities enable us to learn new concepts, emotional intelligence is crucial in our relationships with people. A candidate with strong emotional intelligence works well in a team and can discern others’ emotions to make better decisions.
The main difference between cognitive intelligence vs. emotional intelligence and emotional quotient is that the former helps us learn new concepts, and the latter is crucial for our relationships with people.
Let’s quickly review emotional intelligence vs. cognitive intelligence differences:
| Cognitive intelligence | Emotional intelligence |
Skills | - Analytical thinking - Logical reasoning - Problem-solving abilities - Abstract thinking | - Self-awareness - Empathy - Emotional regulation - Social skills |
Benefits | - Efficient learning and application of new information - Strategic planning and decision-making - Effective problem resolution | - Improved communication and collaboration - Conflict resolution - Leadership and team building |
Importance in the workplace | - Supports productivity and innovation - Facilitates better decision-making - Critical for roles that require complex analysis and technical skills | - Creates a positive work environment - Enhances team cohesion and morale - Vital for leadership roles and customer-facing positions |
Potential | - Relatively stable over a person’s lifetime | - Can be developed with training and practice |
A candidate with strong emotional intelligence works well in a team and can discern others’ emotions to make better decisions. You can hire for emotional intelligence using:
Personality and psychometric tests such as our DISC Personality test
Behavioral interview questions
Job simulations
The good thing is that emotional intelligence isn’t a fixed trait, which implies that companies can create targeted training and self-awareness exercises to help employees enhance their emotional intelligence. Using this fluid intelligence, they can contribute to a more collaborative and productive workplace where individual differences can thrive.
What types of cognitive tests are there?
Employers have long used tests to measure cognition vs. intelligence and determine whether a person is a good fit for the job. Today, these assessments are more advanced and accurate than ever before.
At TestGorilla, we offer a variety of cognitive ability tests to evaluate your candidates accurately. You can combine them with role-specific assessments and personality tests to evaluate an applicant’s skills, cognitive intelligence, and emotional intelligence.
Here are our different types of cognitive tests:
Problem Solving test
The Problem Solving test evaluates an applicant’s ability to interpret data and apply logic to come to conclusions and make decisions. Candidates with good problem-solving abilities can use their analytical skills to solve complex problems.
This cognitive intelligence test is particularly beneficial for roles that demand quick thinking, adaptability, and efficient problem resolution under pressure. They include administrative assistants, project managers, planners, and positions in hospitality or sales.
For example, when hiring for a project management position, candidates who score well on this test are likely to excel in managing project timelines, allocating resources effectively, and navigating unforeseen challenges during project execution.
Explore TestGorilla's Problem Solving test
Explore and assess your candidates with TestGorilla's Problem Solving test.
Critical Thinking test
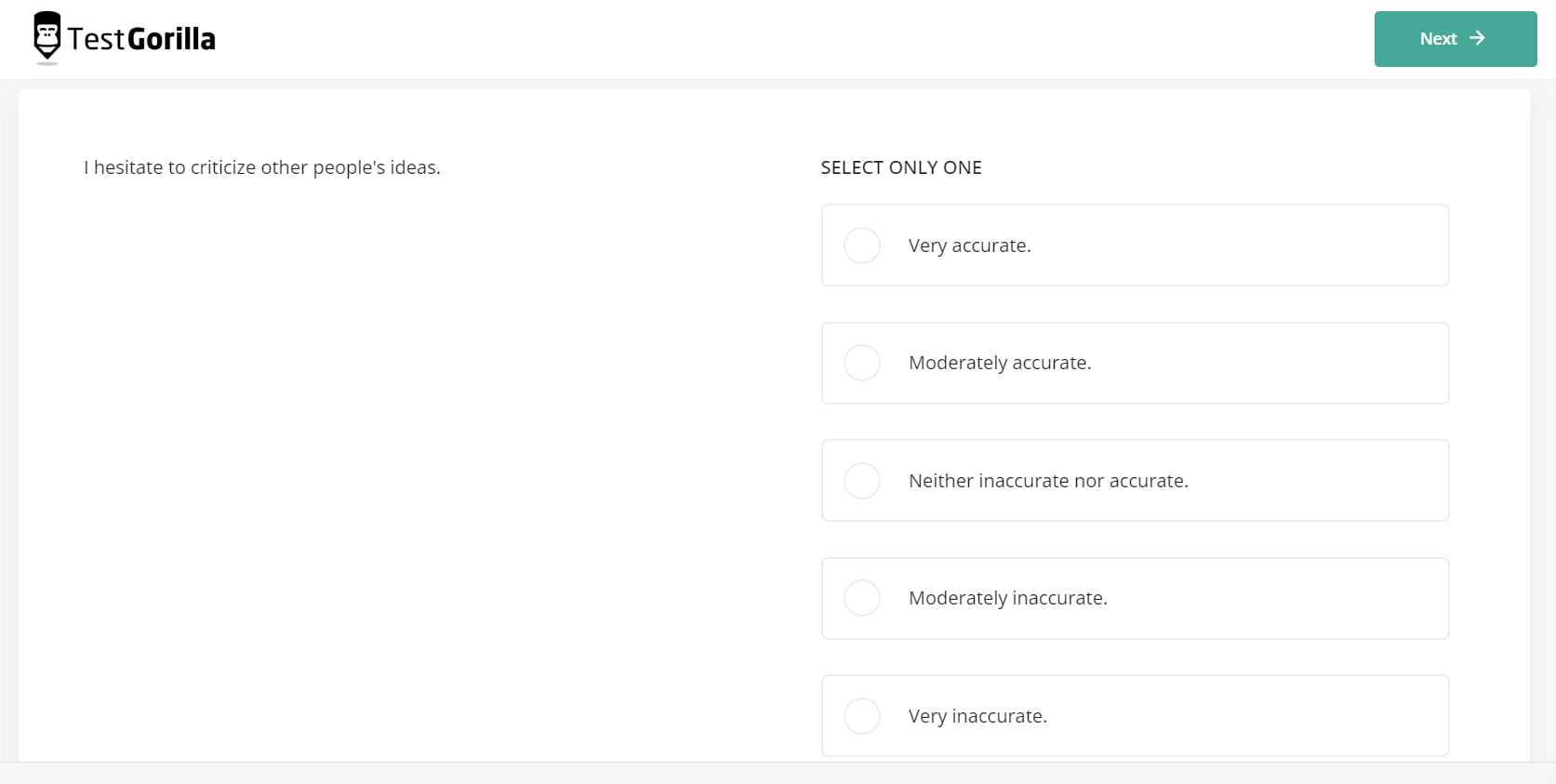
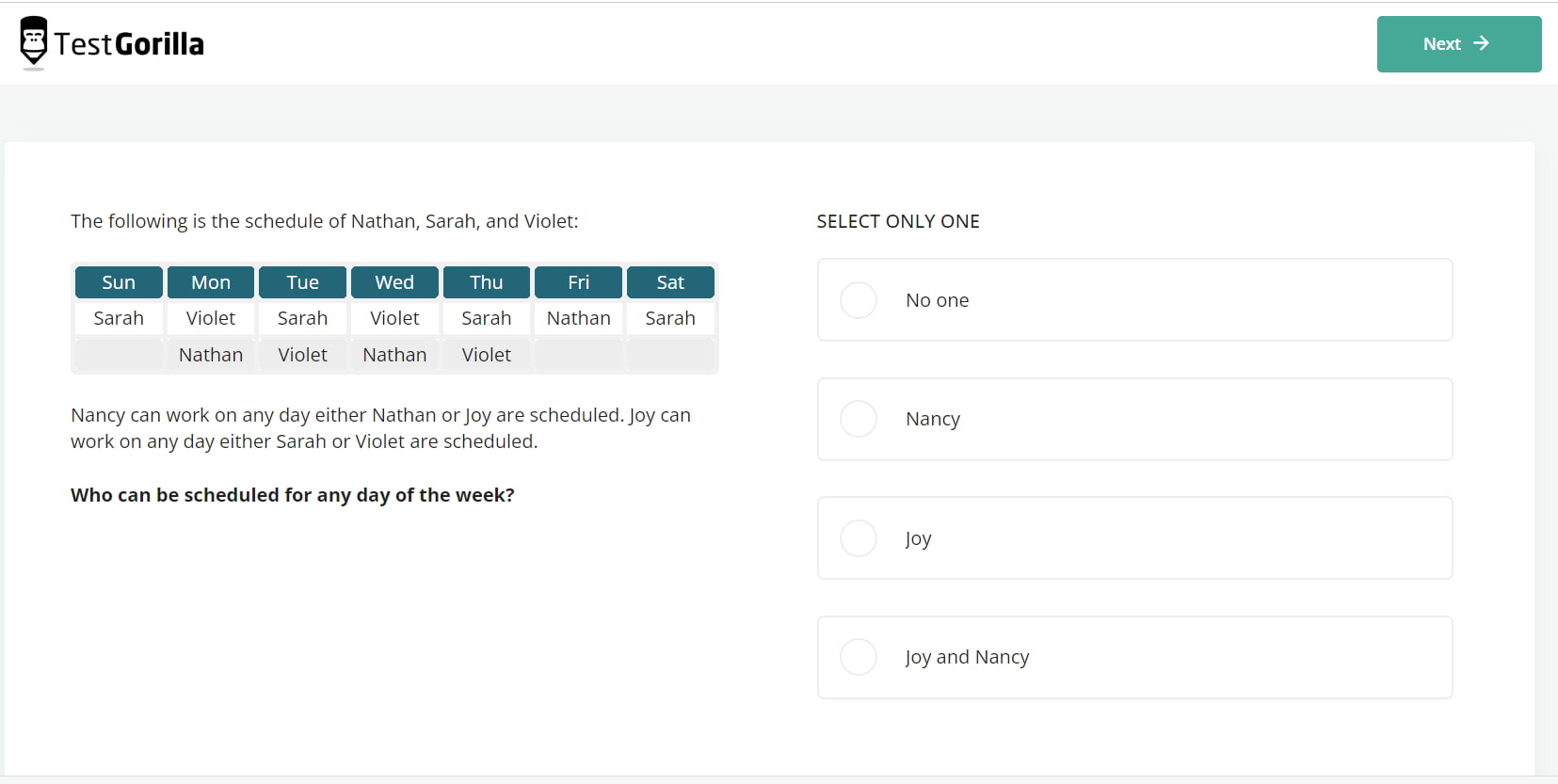
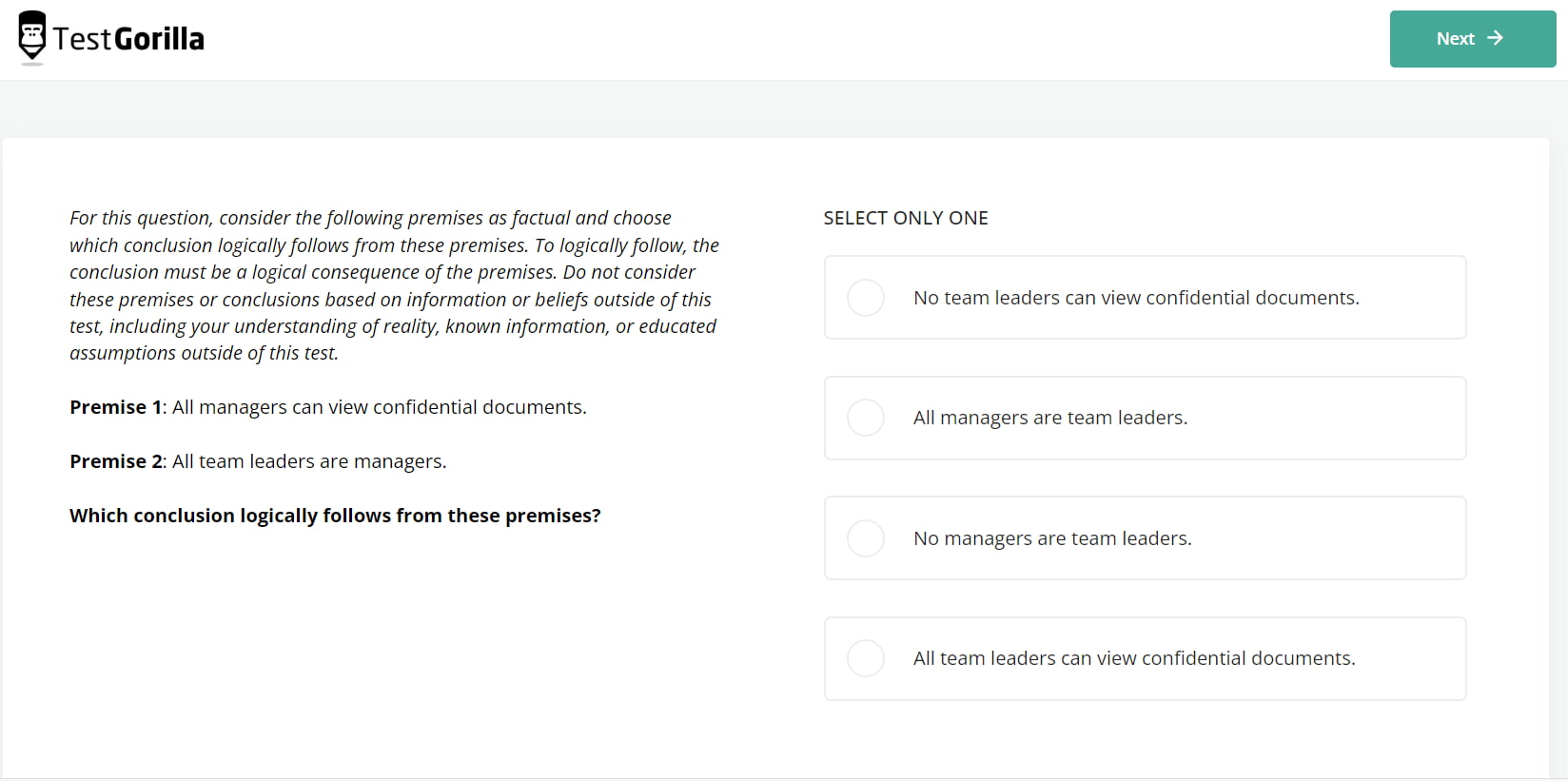
The Critical Thinking test uses inductive and deductive problems to evaluate candidates’ critical-thinking abilities. Those who score well on this test can use their analytical skills to make solid judgments without biases and understand cause-and-effect relationships.
You can incorporate this cognitive intelligence test early into your hiring process for positions such as analysts, legal professionals, executives, and data scientists.
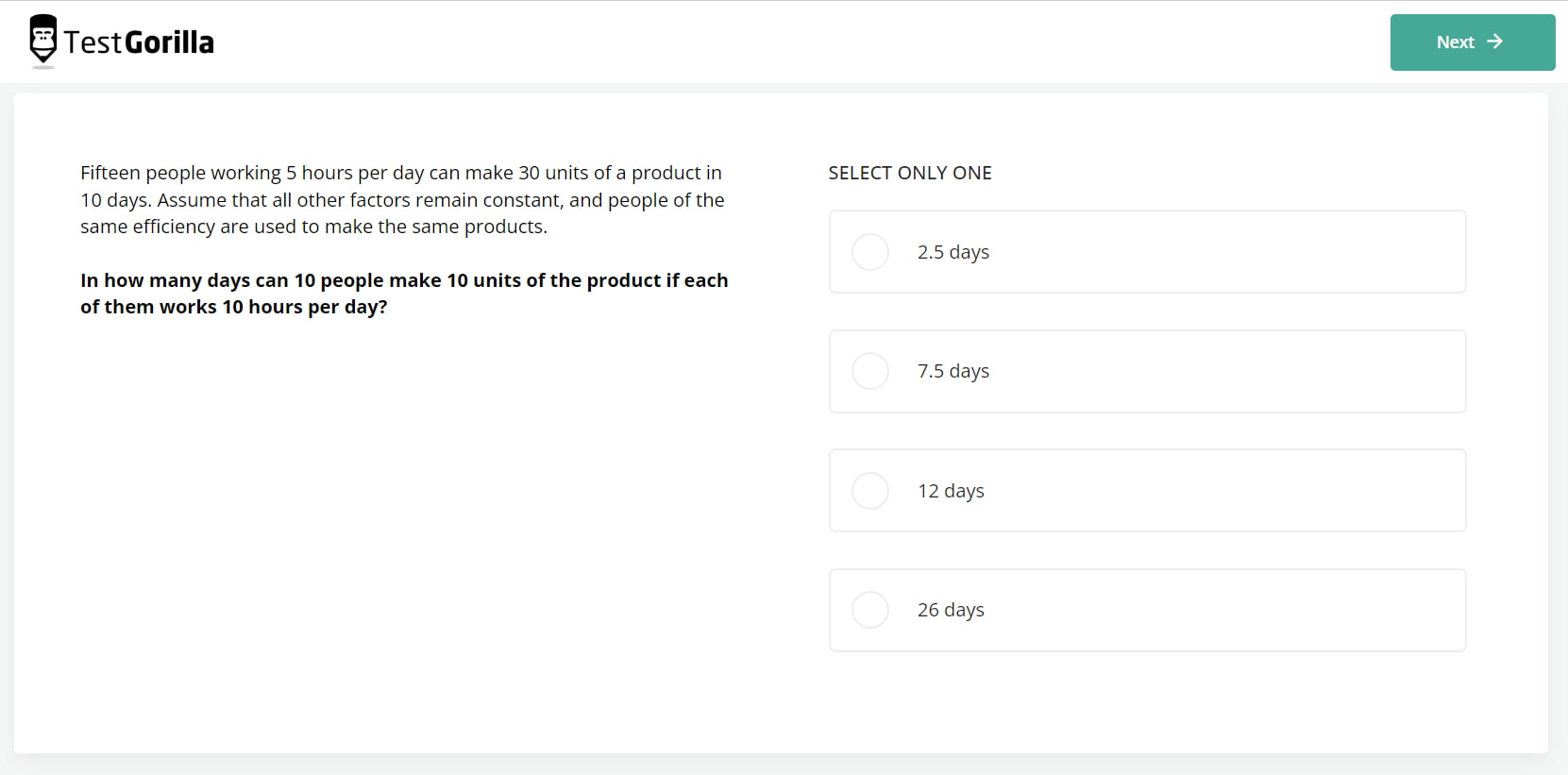
This 12-minute test leans more toward cognition vs. intelligence by challenging candidates to navigate complex syllogisms, sequences, and arrangements and draw sound conclusions. Here’s an example:
If you want to view more questions included in this test, check out the Critical Thinking test preview.
Verbal Reasoning test
TestGorilla’s Verbal Reasoning test identifies candidates who can find analogies and attribution and recognize relationships between words. Job seekers who do well on this test are capable of drawing conclusions from written text.
You can use this test to find candidates with great language-based analytical skills necessary for content creation, report writing, legal analysis, and any role where interpreting and producing complex documentation is a key responsibility.
This 10-minute test measures cognition vs. intelligence by tasking candidates with linguistic puzzles and text-based logic problems.
Reading Comprehension test
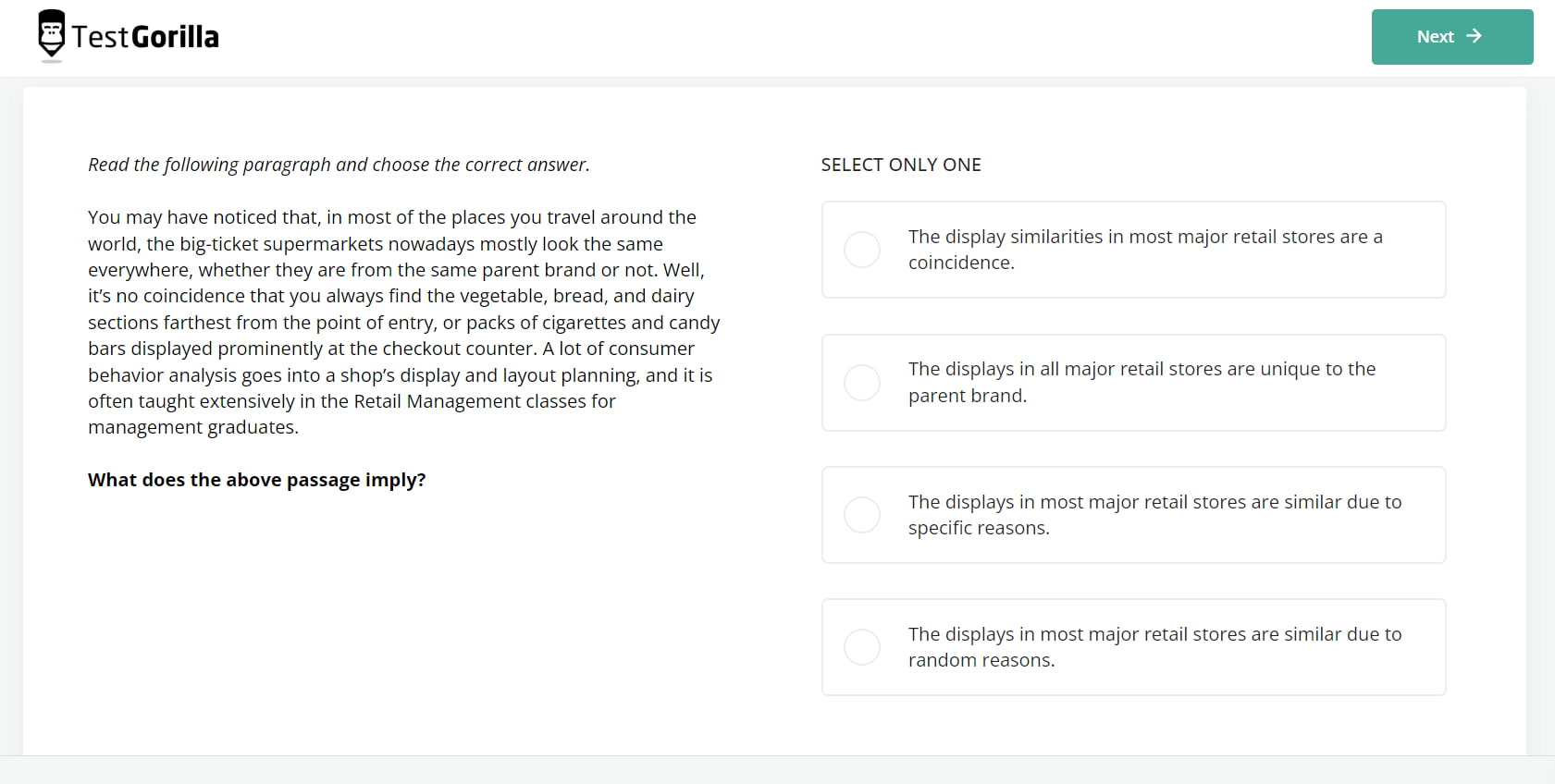
The Reading Comprehension test evaluates whether applicants can comprehend the contents of written text. It identifies candidates who can grasp the main idea behind a text and reach conclusions based on their understanding.
You can incorporate this cognitive intelligence test into the hiring process for positions where interpreting and synthesizing written information is a regular task, including editors, analysts, and managers.
Numerical Reasoning test
The Numerical Reasoning test assesses candidates’ ability to find and interpret patterns in numbers. Strong numerical reasoning is important for jobs that deal with finance and accounting, such as financial analysts, investment bankers, and accountants.
In this intermediate difficulty test, candidates have 10 minutes to answer 12 questions that measure how well they perform calculations, apply numerical data to solve problems, and identify trends effectively.
Those who score well can interpret text, tables, charts, graphs, and diagrams.
Attention to Detail test
The Attention to Detail test reveals which candidates can pay attention to and draw information from images. It’s perfect for assessing applicants for roles like graphic designers, marketers, and lab technicians.
This intermediate-level test, with a 10-minute duration, challenges candidates to show their visual attention to detail through various tasks.
Use cognitive tests during recruitment to make better hiring decisions
Strong intelligence is the key to success in every job, regardless of role-specific skills. Candidates and employees who possess emotional and cognitive intelligence are the ones you should pay the most attention to in your hiring process.
With our cognitive tests, you can assess candidates’ cognitive skills, such as problem-solving, critical thinking, and verbal reasoning.
If you want to see how our platform can help you make more accurate hiring decisions and recruit an exceptional workforce, book a live demo.
You can also take a product tour and learn more about the functionalities of our tests and how to customize them.
However, the best choice is to sign up for a free account and start using the Problem Solving test today to find intelligent candidates for your open roles.
Cognitive intelligence FAQs
If you still have questions about the difference between intelligence and cognition, you can find answers below.
Are IQ and cognitive intelligence the same thing?
Intelligence quotient (IQ) and cognitive intelligence are not quite the same. The difference between intelligence and cognition is that IQ scores aim to quantify cognitive skills such as reasoning, problem-solving, and understanding complex ideas. In contrast, cognitive intelligence encompasses a broader range of mental capabilities, including memory, attention, and language understanding. Cognitive skills assessments can predict a candidate’s job performance, while job IQ tests are obsolete in hiring.
What is the difference between cognitive and emotional intelligence?
Cognitive intelligence involves logical reasoning, problem-solving, and learning abilities, which are essential for tasks requiring analytical thinking. Emotional intelligence encompasses the ability to recognize, understand, and manage emotions, which is crucial for effective communication and interpersonal relationships. Emotional intelligence vs. cognitive intelligence centers around different types of skills.
American authors like Peter Salovey, Daniel Goleman, and John D. Mayer looked into emotional intelligence in depth. On the other hand, Thomas J. Bouchard, Robert Sternberg, David Wechsler, and Mary E. Johnson focused on cognitive intelligence and neural networks.
What is the difference between cognition and intelligence?
The main difference between intelligence and cognition is that you can learn and develop new skills by having strong cognitive intelligence. On the other hand, your general intelligence stays at around the same level throughout most of your life based on what you learned as a child and an adolescent.
What are the 3 cognitive models of intelligence?
Analytical intelligence: The ability to analyze existing information to solve problems using critical thinking and cognitive reasoning
Creative intelligence: The ability to innovate and come up with ideas to overcome new challenges
Practical intelligence: The ability to apply knowledge and skills to address real-world issues and practical problem-solving
How to increase cognitive intelligence?
Exercise regularly
Engage in brain-training games and puzzles
Manage stress with relaxation techniques
Practice mindfulness and meditation
Learn a new language
Get enough sleep
Maintain a nutritious diet
Socialize and engage in meaningful conversations
Explore creative hobbies like music, art, or writing
Read regularly to expand your knowledge
Seek new experiences
Related posts
Hire the best candidates with TestGorilla
Create pre-employment assessments in minutes to screen candidates, save time, and hire the best talent.
Latest posts
The best advice in pre-employment testing, in your inbox.
No spam. Unsubscribe at any time.

Hire the best. No bias. No stress.
Our screening tests identify the best candidates and make your hiring decisions faster, easier, and bias-free.
Free resources
This checklist covers key features you should look for when choosing a skills testing platform
This resource will help you develop an onboarding checklist for new hires.
How to assess your candidates' attention to detail.
Learn how to get human resources certified through HRCI or SHRM.
Learn how you can improve the level of talent at your company.
Learn how CapitalT reduced hiring bias with online skills assessments.
Learn how to make the resume process more efficient and more effective.
Improve your hiring strategy with these 7 critical recruitment metrics.
Learn how Sukhi decreased time spent reviewing resumes by 83%!
Hire more efficiently with these hacks that 99% of recruiters aren't using.
Make a business case for diversity and inclusion initiatives with this data.