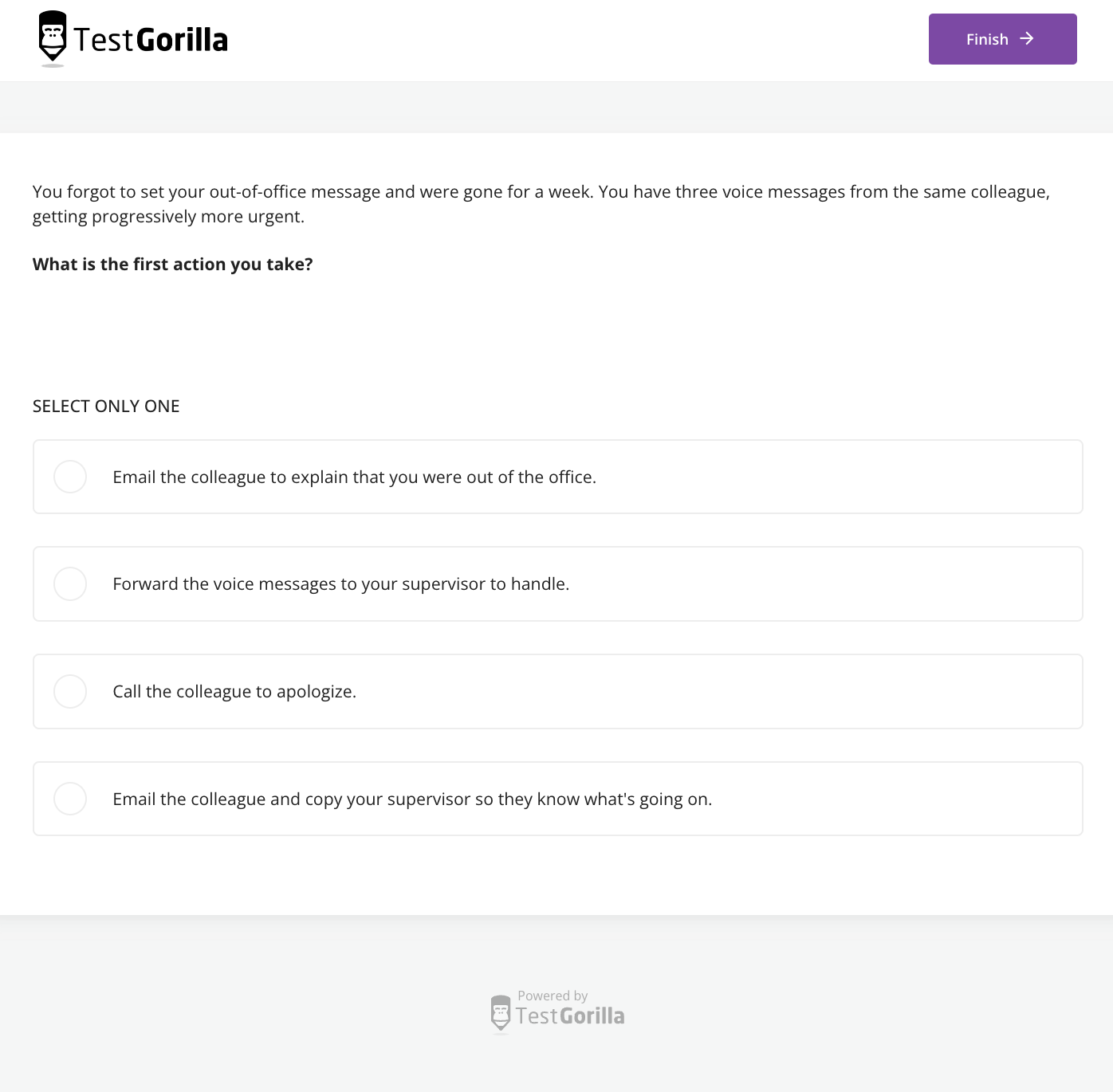
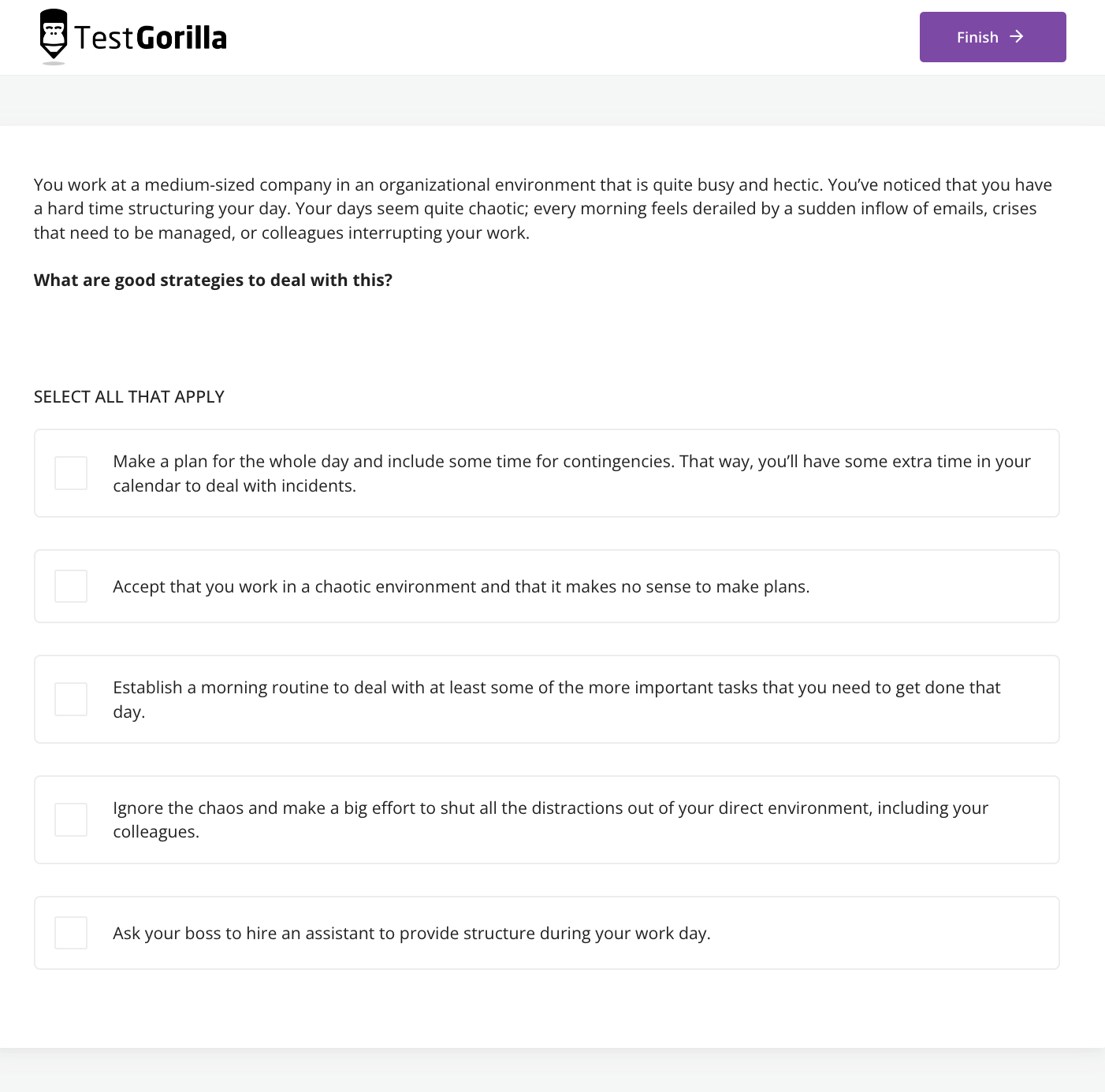
Proofreading is more than just giving a piece of writing a quick check-over for misplaced apostrophes. Professional proofreaders ensure content is appropriate and easy to understand, needing a thorough eye for detail and understanding of the English language.
But that’s not all – talented proofreaders are also objective, motivated, and great team players. Without these skills, technical talent only goes so far, and you can’t measure these effectively with experience checks alone.
Employers can, however, measure proofreading skills reliably with talent assessments.
Below, we explore nine proofreader skills all applicants should develop and that recruiters should prioritize when building a proofreader test.
Table of contents
9 fundamental proofreader skills employers look for
We recommend the following skills for proofreading success:
Linguistic knowledge
Attention to detail
Critical thinking
Motivation and self-discipline
Communication
Time management
Technical knowledge and adaptability
Sticking to a style guide
Research
If you’re hiring for these skills, skip ahead to the next section and find out what to include in your proofreader test.
In the meantime, let’s break down these skills and why they’re so valuable.
1. Linguistic knowledge
Since proofreaders work intensively with words and punctuation, they need strong reading and writing skills that go beyond finding simple common mistakes. They must be able to quickly recognize misspellings and grammatical errors in written content and then fix and explain those mistakes.
In an age where some companies use artificial intelligence (AI) for revising written work, studies show that skilled human proofreaders are still much more effective at grammatical accuracy and content planning.
Strong language and content skills help successful proofreaders improve copy so it’s easy to read, adheres to brand style guides, and presents a professional face.
These are important for businesses because customers see bad grammar and spelling as unprofessional and untrustworthy. Studies show that online advertisements with mistakes and typos lose up to 70% of their potential customers.
2. Attention to detail
To keep the text error-free, proofreaders must read each line of copy slowly and carefully.
Industry experts claim proofreaders likely need to process around 3,000 words per hour, although this can vary depending on the project.
However, it’s not work you should rush. As Rosemary Shipton writes in her essay “The Mysterious Relationship: Authors and Their Editors,” editing professionals are expected to account for around 95% of all errors in the text.
A proofreader with a strong eye for detail might notice a document uses Oxford commas when a style guide advises against them, has hyphens in place of em dashes, or interchangeably switches between first-person to second-person narrative.
Attention to detail is a skill that proofreaders improve through efficiently organizing their schedules, minimizing distractions, and creating technical checklists.
3. Critical thinking
Critical thinking in proofreading is all about making unbiased decisions that obey style guides.
For example, sometimes, more than one way of phrasing an idea is technically correct, though very few of them fit the writing brief.
Therefore, proofreaders with strong critical thinking skills decide which sentences and phrases make the most sense in any given context.
Thinking critically when proofreading also means being decisive with the words used. If there's a more concise way to get a message across, the best proofreaders know what to remove.
Proofreaders develop this skill by asking insightful questions of their clients and reflecting on their thought processes.
4. Motivation and self-discipline
Becoming a proofreader means being a self-starter and often working independently when reviewing text. A proofreader needs to be motivated to stay on task and complete projects.
Since they’re often the last line of defense against mistakes, proofreaders might not always have someone else to turn to for answers. Therefore, they have to be independent thinkers.
Freelance proofreaders have even more independence. They don't have supervisors present and often work on several projects through their proofreading services simultaneously.
Self-disciplined proofreaders give each piece of work the same attention and effort, meaning its quality is consistently high.
5. Communication
Whether proofreaders work alone or within a team, they need to communicate effectively with writers, clients, and colleagues.
Communication skills keep documents moving efficiently through the editorial process. Proofreaders often work on various teams or multiple projects, too, so they have to be able to communicate in ways best suited for the person they’re talking to.
Proofreaders can develop communication skills by listening actively to requests and even applying their proofreading logic to their own communication channels.
6. Time management
Written material usually reaches proofreaders just before it’s published online or goes into design. That means there’s usually pressure on them to turn around text quickly, and some professionals juggle multiple projects.
Proofreaders have to prioritize their work to meet deadlines. They usually manage their time themselves, especially if they work remotely, and must find ways to stay focused.
Healthy time management skills ensure proofreaders are more productive and precise because they're well-rested and motivated to do their best.
7. Technical knowledge and adaptability
The best proofreaders are highly flexible and confident when using various tools to check text and make comments. Much like how accountants use calculators, proofreaders must use tools like spell-checkers wisely and to their maximum potential.
Mainly, good proofreaders need word processor skills that can carry over across different programs such as Microsoft Word or Google Docs.
They also work with PDF files and markup software to make comments and changes to text already in the design process.
It’s also useful if proofreaders are familiar with collaboration and meeting tools, such as Zoom and Slack, so they can connect with the editorial team.
8. Sticking to a style guide
Every proofreading project should have a style guide that covers elements such as international vocabulary, tone of voice, branding elements, and formatting.
Proofreaders must be flexible and work within the guidelines set for each project. That means being willing to adapt their knowledge and skills to fit a brand's needs.
In marketing and journalism, for example, many projects require writers and proofreaders to use the concise and direct Associated Press stylebook, but other projects may require following the Chicago Manual of Style.
Attitude is just as important as skill here, meaning proofreaders must willingly respect the guidelines set for them.
9. Research
Although much of the work proofreaders do takes place on-page, they need to be ready to find different resources beyond the writing process.
For instance, a proofreader editing social media marketing for the first time could benefit from researching the etiquette required for this type of writing. There’s always room to develop.
Proofreaders must be ready to balance physical editing with research and referencing. It's an ideal role for people who are highly skilled with words but who are always willing to learn.
How to assess editing and proofreading skills
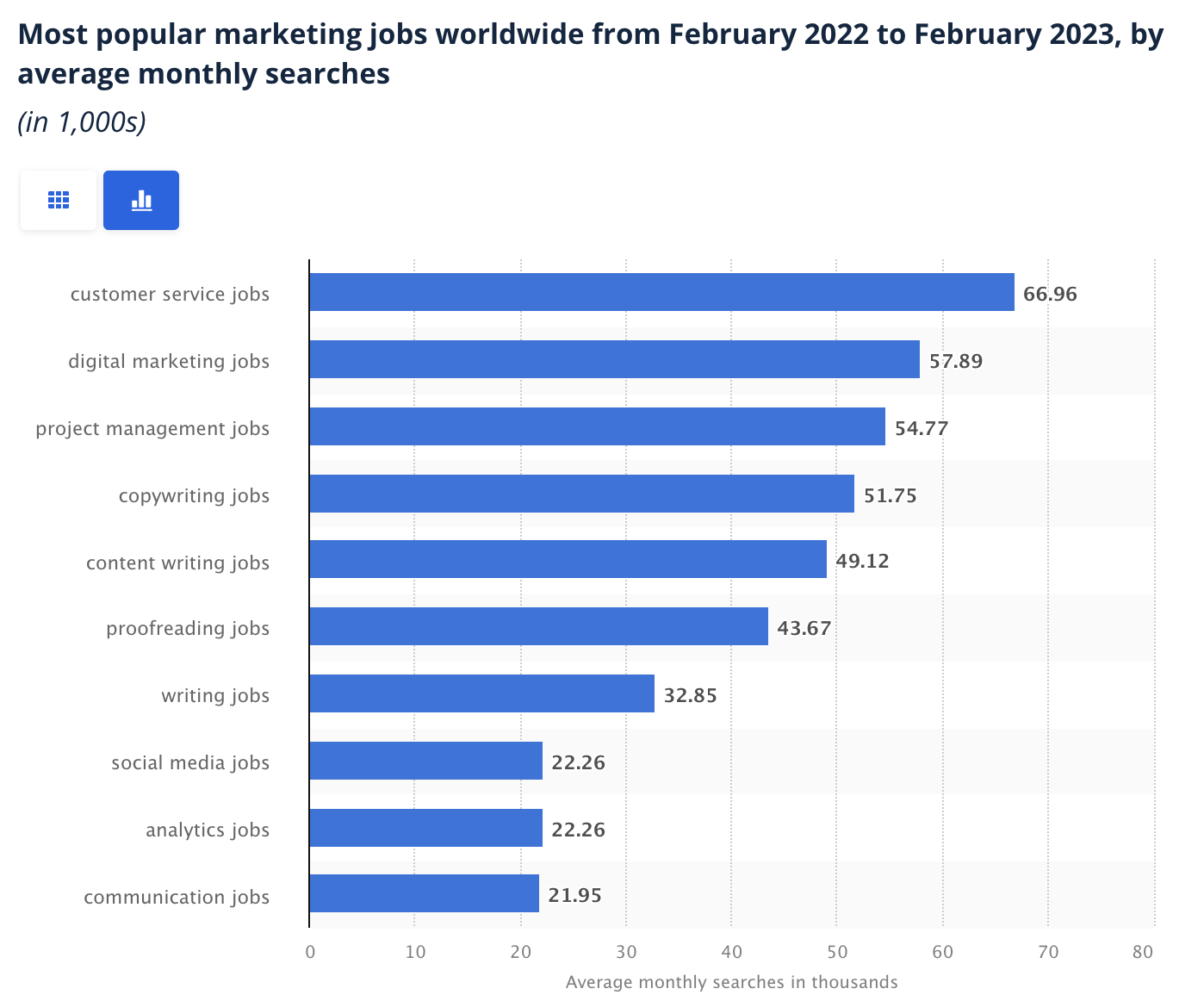
There are plenty of people out there looking for proofreading jobs. It’s one of the six most-searched-for marketing roles online:
However, you need to cut through the pack to find talented individuals with proven proofreading and editing skills.
When recruiting for a proofreader, let applicants show you what they can do rather than tell you through resumes.
Take the example of Contentoo, a content marketing firm that regularly hires online proofreaders. Since moving to TestGorilla, the company has confirmed that its hiring process is more motivational for candidates. Now, applicants feel more pushed to "achieve something" and move ahead.
Skills-based hiring is objective, reliable, and efficient. By testing proofreader candidates with specialized assessments, you learn more about how they attack problems.
Let's look at how you can assess proofreading and editing skills during recruitment and how TestGorilla's assessment library can help.
Linguistic knowledge
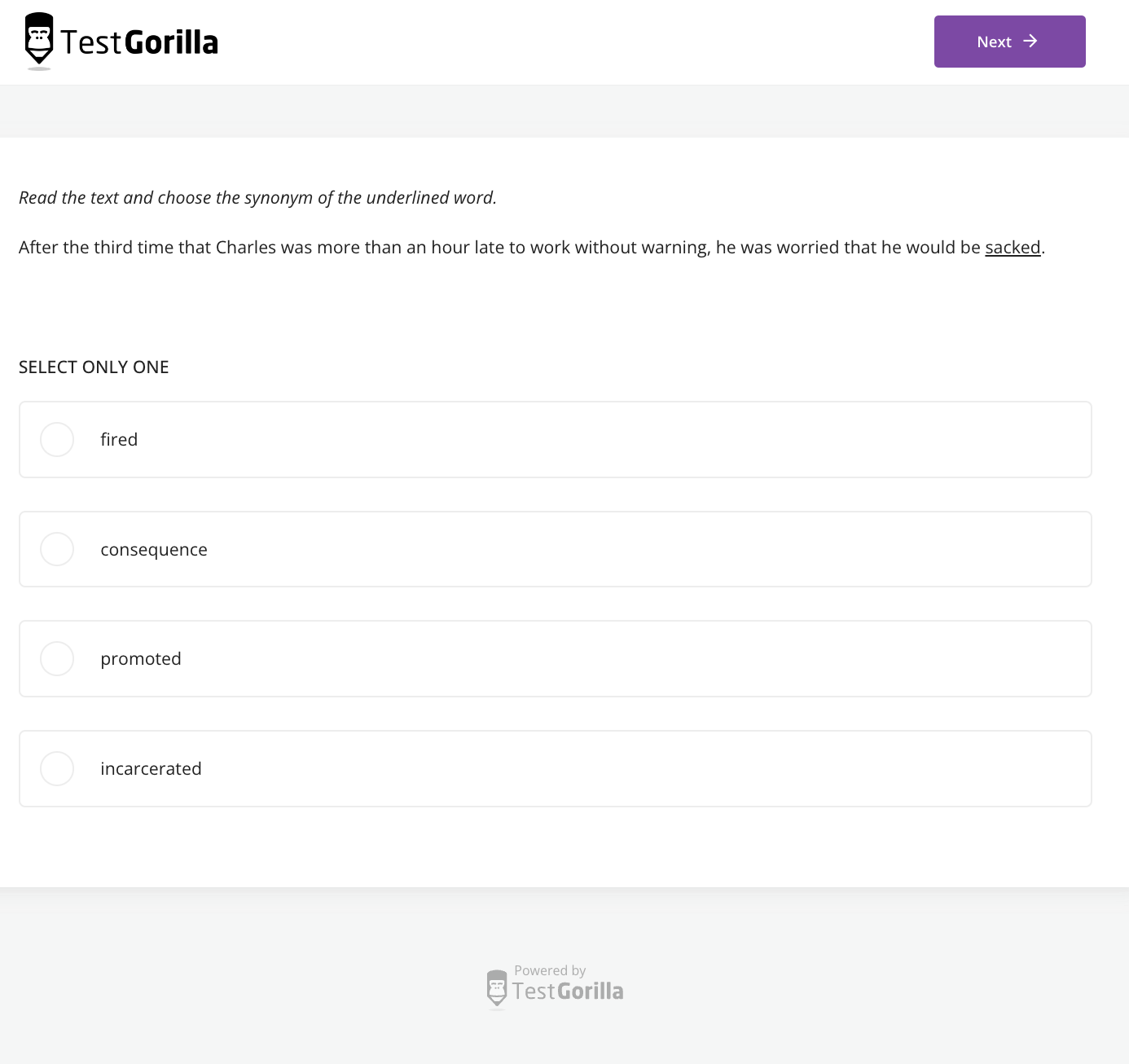
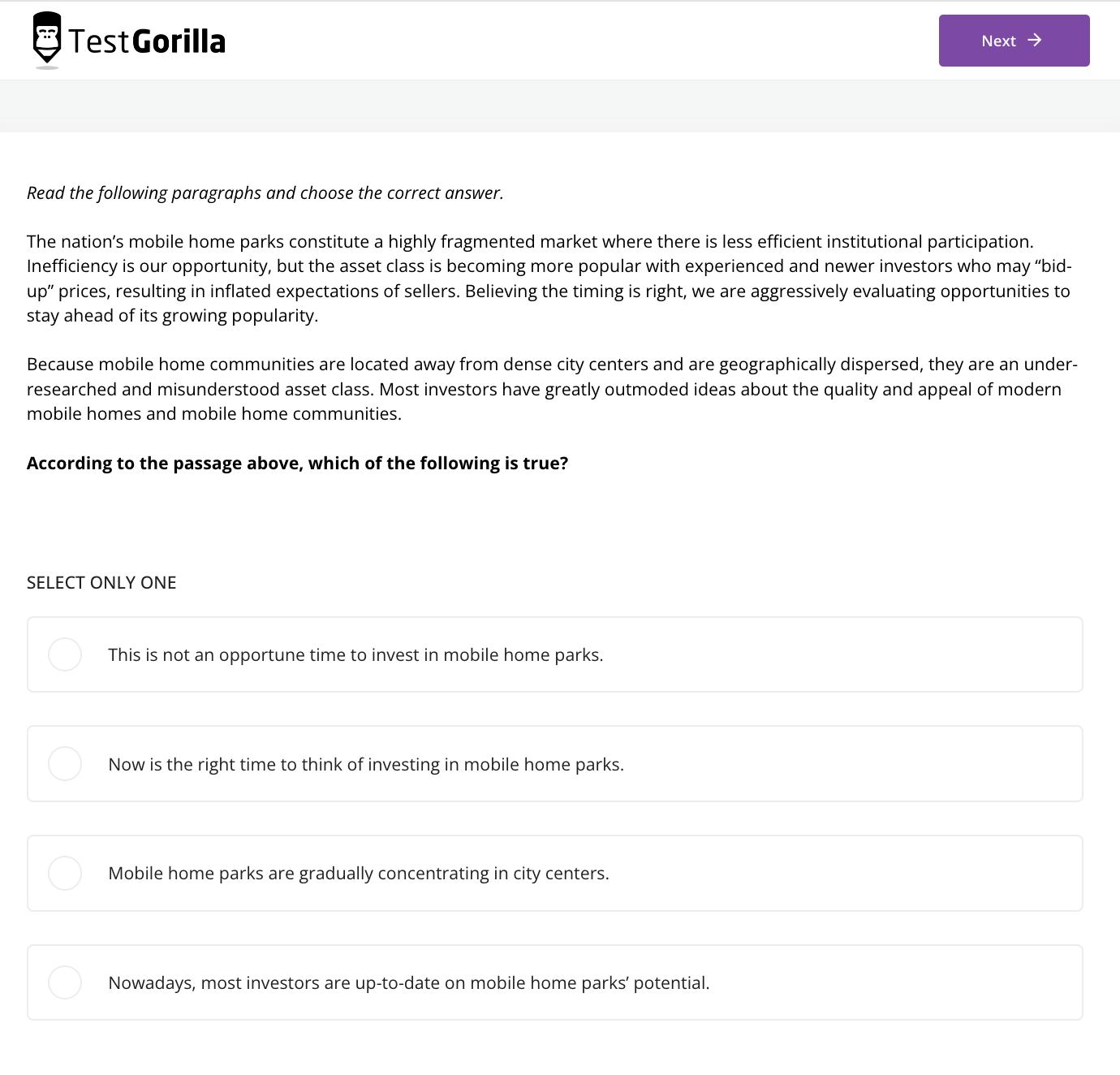
It's wise to test candidates' mastery of the specific languages you need them to work with. You could use our English (proficient/C1) test for proofreading in English, for instance.
This proofreading assessment tests applicants’ grammar knowledge, writing competence, and vocabulary scope:
If you work in more languages, feel free to book a 30-minute demo with TestGorilla and explore our library further.
Attention to detail
Attention to detail is reasonably easy to measure by asking applicants to complete trial exercises.
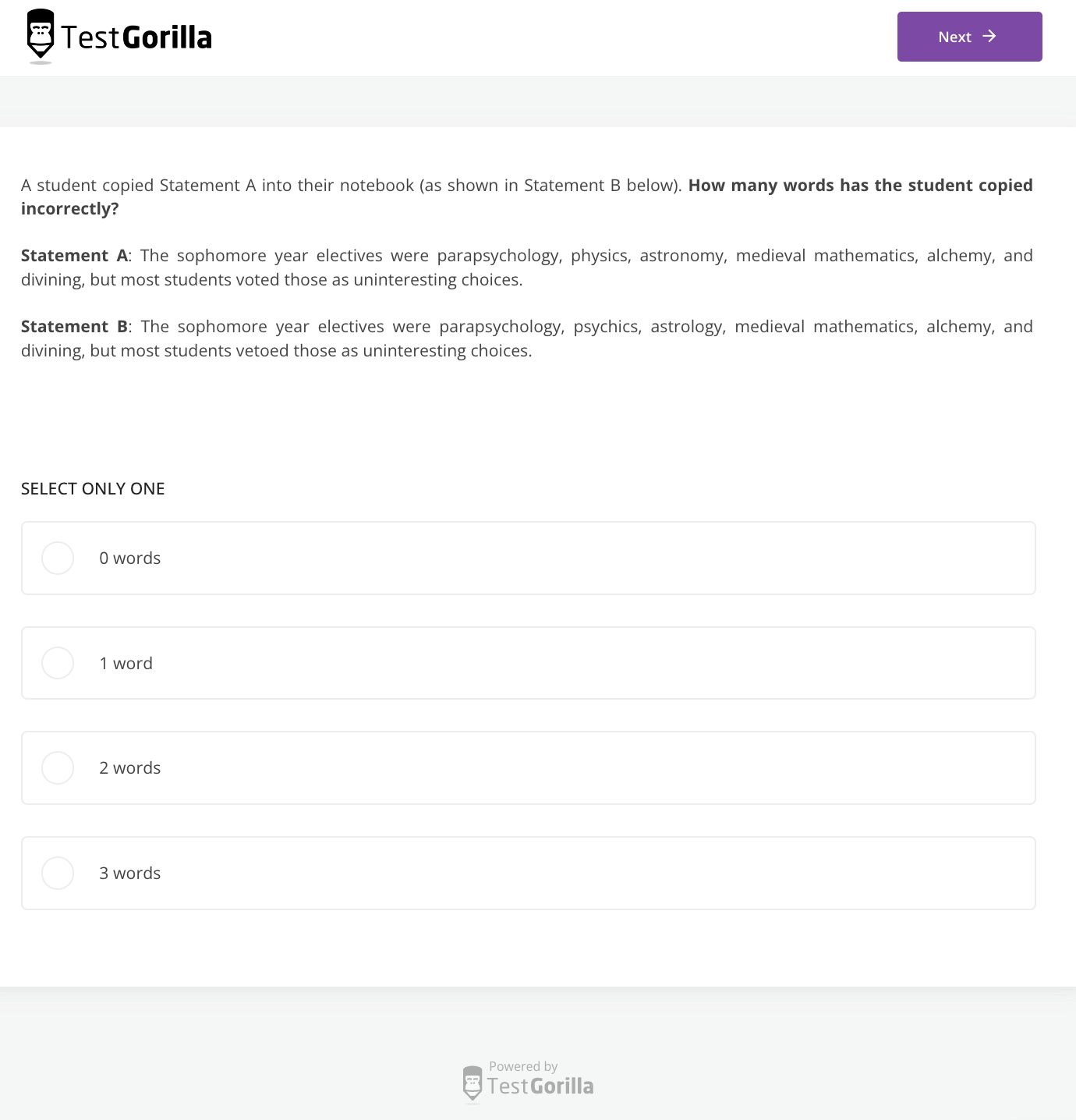
Beyond this, we recommend running the Attention to Detail test. You can use this proofreading assessment test to measure an applicant’s ability to double-check for the consistency of information, compare two versions of a text, and filter information:
Critical thinking
Again, you could test a candidate’s ability to think and proofread objectively with a trial article or run proofreading tests.
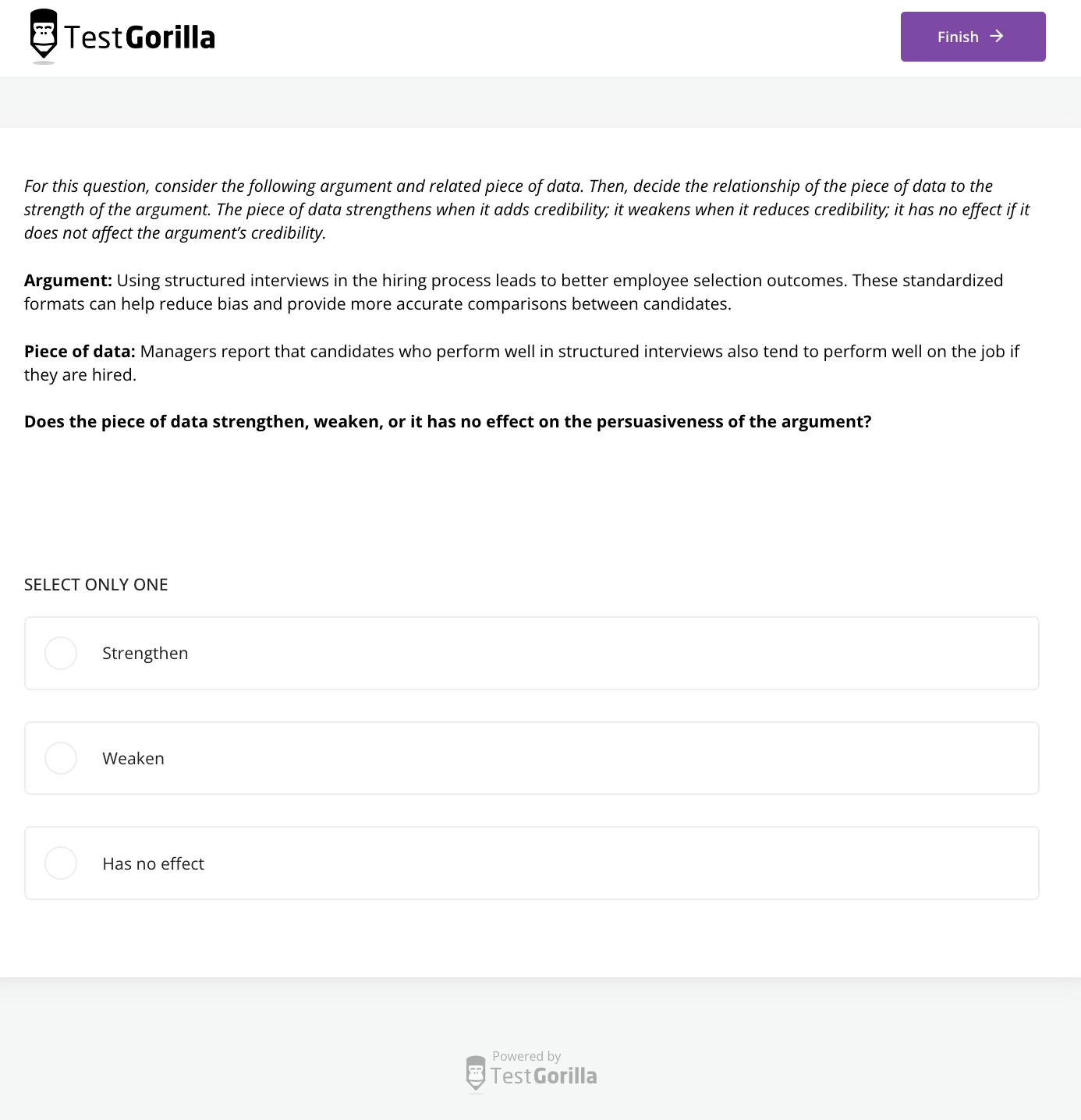
The Critical Thinking test accurately measures how well proofreaders can resolve problems they encounter.
This test evaluates how well a candidate can analyze data, make decisions independently, and think critically when expected to make arguments:
It’s a generic talent assessment that helps you find candidates with the ability to complete tasks independently and resolve job challenges effectively.
Motivation
TestGorilla’s Motivation test is another generic assessment that grades people on their ability to self-start and manage their own workloads. It also measures how well a candidate aligns with your job profile.
This test is highly customizable, meaning you can adjust it to fit the profile of a proofreader and find talented people who are enthusiastic to work with you. You can learn more about this in our product tour.
Hire the best proofreaders with TestGorilla
Ready to hire the best proofreaders with TestGorilla’s talent assessments?
Communication
The Communication skills test evaluates how well applicants interpret written communication and how effectively they can summarize their ideas and recommend the next steps.
This test also evaluates professional etiquette, so you can be sure your proofreader communicates requests for edits kindly:
In addition, the test measures a candidate’s ability to understand non-verbal cues and listen actively. These are important traits for any proofreader attending online meetings.
Time management
Testing proofreaders on time management is important because you can’t afford to wait forever for clean copy.
We recommend offering a trial project, setting a clear deadline, and checking to see which candidates are the most punctual.
Then, ask your candidates insightful questions regarding how they approach projects and tasks. The easiest way to get started is with our Time Management test.
This test measures how well applicants can plan, prioritize, and finish tasks on time. This test also measures communication, reflection, and execution.
Software
Proofreaders need to use advanced features on current versions of the tech you use to create and distribute content. That means testing their knowledge of word processors, content management systems, and editing tools.
When hiring remote proofreaders, consider prioritizing applicants skilled in Microsoft Word and Google Docs, two of the most commonly used word-processing tools to create and collaborate on content.
Our Microsoft Word test measures whether proofreaders can make comments, track changes, fix formatting issues, add page numbers, and create headers and titles.
To explore a sample test, click here and get a preview of the type of Word-related questions you’d be asking candidates to answer.
Style guides and research
You can use several TestGorilla assessments to measure how skilled proofreaders are at understanding and following detailed style guides or instructions and how they read and use the information they find during research.
For instance, the Reading Comprehension test measures how effectively a candidate understands written instructions and content.
This is important if you have a highly specific style guide and want to determine whether an applicant follows instructions by directing them to only proofread a portion of text, for example.
Meanwhile, our Verbal Reasoning test helps to measure how well candidates draw conclusions from written material, find analogies, and understand written information in-depth.
The 9 key skills for proofreading and how to test for them
Let’s quickly summarize the skills required for proofreading and how recruiters can measure them.
Skills of a proofreader | How to assess proofreading skills via TestGorilla |
Linguistic knowledge | English (proficient/C1) test and further language variants |
Attention to detail | Attention to Detail test |
Critical thinking | Critical Thinking test |
Motivation and self-discipline | Motivation test |
Communication | Communication and Communication (Intermediate) tests |
Time management | Time Management test |
Technical knowledge and adaptability | Specialized tests such as Adobe Illustrator and Microsoft Word |
Sticking to a style guide | Reading Comprehension and Verbal Reasoning tests |
Research | Reading Comprehension and Verbal Reasoning tests |
Proofreading skills: More than just an eye for detail
As you can see, hiring a proofreader isn't just a case of choosing someone good with words. You also need someone with excellent time management, critical thinking, communication, and attention to detail.
Like Contentoo, you can use TestGorilla skill assessments to make better-informed and more incisive proofreader hiring decisions. Take a product tour and see our testing platform and proofreading tests in action.
Want a bit more detail? Be sure to sign up for a free demo for the complete lowdown.
And now you know how to assess proofreading skills, we suggest you register for a free forever plan and start grading applicants – with no strings attached.
Skills of a proofreader: FAQs
Let’s close with some common questions about skills for proofreading and why they’re important.
What skills do you need to proofread?
We recommend the following skills required for proofreading:
Expert knowledge of linguistics
Self-motivation and discipline
Strong interpersonal communication
Technical adaptability
Knowledge of different editing styles and guidelines, such as AP and MLA
Scroll up to the "9 fundamental proofreader skills" heading to learn more about these skills and why they’re important.
What is a proofreading assessment test?
A proofreading assessment test evaluates job applicants' ability to follow style guides and identify and fix grammatical mistakes. It can also determine if an applicant knows proofreading conventions and common software programs used on the job. An editing and proofreading skills assessment should also evaluate your ability to communicate effectively, collaborate with others, and take direction.
What makes a great proofreader?
A great proofreader has solid grammar, formatting, spelling, and punctuation knowledge in their chosen language. They're also reliable self-starters who manage their own projects and deadlines and make critical, unbiased decisions in accordance with style guides. A great proofreader is confident working independently and with others, and is an open communicator with people at all levels of their team.
What are the three main focuses of proofreading?
The three main focuses of proofreading are to address and remove grammar and punctuation errors, improve word choice, and ensure writing is correctly formatted to a brief or style guide. However, this is a job with a lot of nuances that vary from project to project, meaning that what’s a priority for one client’s style guide might not be for another’s.
What is the difference between proofreading and editing skills?
Proofreading focuses on fixing technical errors in writing, such as spelling, grammar, and punctuation mistakes. Editing, meanwhile, focuses on how readable a piece of writing is and if it flows well. Proofreading is usually the last stage of writing checks, taking place after copyediting and before you submit a draft.
We have more information on how to hire an editor in our guide.
What are examples of proofreader skills?
Attention to detail
Editing
Time management
Software management
Spelling
Formatting
Teamwork
Critical decision making
Self-organization
Project management
Other responsibilities, such as fact-checking and narrative flow, typically fall to copy editors, who read and check copy before proofreading skills come into play.
Related posts
Hire the best candidates with TestGorilla
Create pre-employment assessments in minutes to screen candidates, save time, and hire the best talent.
Latest posts
The best advice in pre-employment testing, in your inbox.
No spam. Unsubscribe at any time.

Hire the best. No bias. No stress.
Our screening tests identify the best candidates and make your hiring decisions faster, easier, and bias-free.
Free resources
This checklist covers key features you should look for when choosing a skills testing platform
This resource will help you develop an onboarding checklist for new hires.
How to assess your candidates' attention to detail.
Learn how to get human resources certified through HRCI or SHRM.
Learn how you can improve the level of talent at your company.
Learn how CapitalT reduced hiring bias with online skills assessments.
Learn how to make the resume process more efficient and more effective.
Improve your hiring strategy with these 7 critical recruitment metrics.
Learn how Sukhi decreased time spent reviewing resumes by 83%!
Hire more efficiently with these hacks that 99% of recruiters aren't using.
Make a business case for diversity and inclusion initiatives with this data.