Table of contents
The world of work is changing. While this was true before COVID-19, the worldwide pandemic put many changes into overdrive.
Part of the revolution in the world of work has to do with changing employee expectations. In fact, a quarter of all employees said that they were planning to quit their jobs post-COVID. To keep employees and attract qualified candidates, companies need to evolve into the next generation of organizational management.
Teal organizations, which were slowly growing in popularity before COVID, are now exploding on the scene. They have become a powerful way to ensure that employees stay happy and productive, leading to a more efficient and healthy company.
Read on to find out more about teal organizations and what skills you need to look for in employees to build one.
What is a teal organization?
Teal organizations are widely viewed as the organizational structure of the future. It is the latest evolution of business and leadership where organizations are living systems fueled and driven by purpose.
In the teal organizational structure, companies abandon more traditional hierarchical structures in favor of cooperation and working together as a team towards a common purpose. The concept of teal organizations came from Fredric Laloux’s book, Reinventing Organizations. In his book, he gives an overview of the gradual evolution of organizations using colors.
Red
Probably the earliest structure in the rise of human societies, red uses power and fear to control. In the modern age, this type of organization lives on the fringe of the law. With its cut-throat organization, it’s a lot like a wolf pack. Common red organizations are gangs, mafia, and other groups led by hardened individuals.
Amber
As the world grew more civilized, culture began to turn away from the more violent and animalistic form of organization. Instead, order and hierarchy began to take over and provide people with the organization they needed to be effective. With formal roles and delegation of power, it works much like an army. You can still see this form of organization in government entities, the school system, and large churches.
Orange
In the past couple of hundred years, the concepts of freedom and personal responsibility began to take over the old structures of society. In its place, the use of innovation and meritocracy for leadership, as well as accountability, created a completely different organization of community and business. Structures began to be viewed as machines and gave rise to the modern Wall Street businesses and corporations we see today.
Green
While orange organizations are still a popular structure for business, it is not without issues. Its emphasis on meritocracy leads to a competitive environment that can encourage teammates to turn on each other. In response, green organizations seek the use of cooperation over competition.
The emphasis on equality, solidarity, and tolerance makes green organizations more like a family. This type of structure can be seen at nonprofits, as well as companies like Costco, Starbucks, and Chipotle, where they emphasize social responsibility as a core value.
Teal
While green is one of the more evolved business models, these companies still experience power struggles and organizational gridlock. Businesses need a way to develop further and create the next organizational paradigm. This next stage is what Laloux refers to as teal.
Teal corporations are defined by:
Agile practices. Teal companies can pivot to meet the market’s needs instead of trying to bend the market to reach them. Their focus is on value instead of the bottom line. This emphasis ironically makes them more successful.
Holistic. Companies, management practices, and processes encourage employees to bring their whole person instead of just their “professional selves” to the workplace. Workers that can fully express themselves have more creativity, passion, and enthusiasm in their job.
Independence. Teal emphasizes peer relationships to operate most effectively. Companies with a teal outlook set up structures that encourage autonomy instead of the oversight of management. Power is delegated throughout the organization instead of being held by the few at the top.
For a while, the concept of teal organizations struggled to get off the ground. It was such a fundamental shift that corporations were hesitant to change the entire structure of their organization. Some of the most famous teal organizations around the world include:
Sun Hydraulics
Patagonia
Morning Star
Heiligenfeld
Buurtzorg
However, when COVID hit, companies had no other choice than to step back from the traditional hierarchal models of the past. Employees worked from home and did not have the oversight that they did in-office. They were independent and collaborated from a distance.
To everyone’s surprise, many employees flourished. Employees worked harder to keep their companies afloat and proved their worth through output alone. Many leaders were surprised that there was no nosedive in productivity, instead, they were more productive than ever.
While still not exactly completely teal, there was nevertheless a new era of company structure born. Rather than being closely managed and monitored, employees are more independent and expect more space to get the job done.
In addition, the widespread worker shortage has given employees more power. In place of worrying about being written up or fired, they can be more creative and have more input in the company.
What skills are necessary for a teal organization?
At the core of a teal organization is its people. Instead, there is more emphasis on personal responsibility and peer oversight. This means that the hiring process and employee base are more important than ever.
When it comes to building a teal organization, employees must have six core traits and skills to build up the company. The hiring process should work to ensure that candidates possess them before being offered a position.
Skill #1: Time management
With the previous structures, leaders delegate and oversee where employees spend their time. Management may give some room for independence, but as a whole, workers are given jobs to do and a set amount of time to accomplish it.
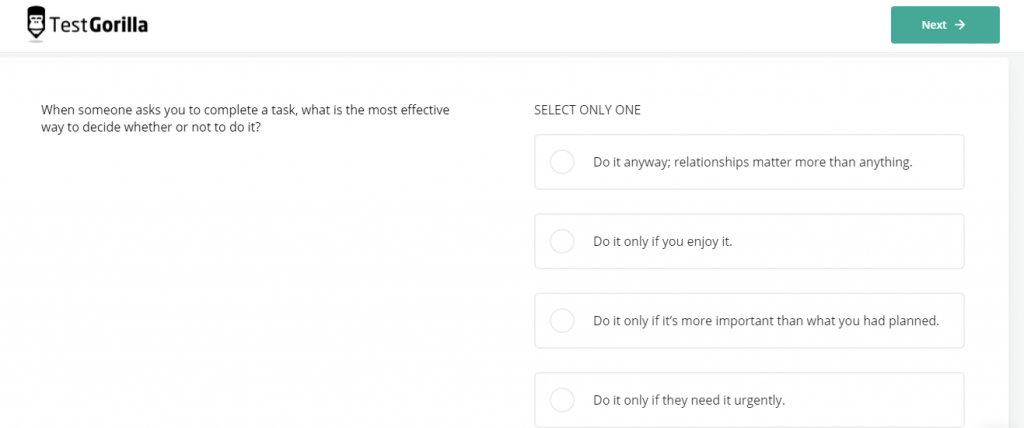
In a teal organization, though, employees are accountable to themselves and their peers. They need to be able to organize their tasks and complete them most efficiently. Time management is no longer handled by leadership, so a time management test is critical in the hiring process.
An example question from TestGorilla’s time management test.
Skill #2: Collaboration
A future employee must be a team player. Cooperation is a core trait of a teal organization. It requires that workers collaborate well together and don’t require too much oversight when they work as a group.
Certain personality types do well in a collaborative environment, and effective communication skills are essential. Ensuring that candidates have these skills and traits will help foster a productive work environment.
Skill #3: Self-disciplined
Without close management, employees need to be motivated to work on their own. They also need to keep on task without someone there to constantly make sure they’re working. While peer accountability is a significant feature in the teal structure, co-workers have little power to provide motivation and keep others on task. Instead, that needs to come from within the workers themselves.
Self-discipline is a critical skill in a teal organization. Intrinsic motivation, as opposed to fear of punishment, needs to drive them. A strong work ethic and self-discipline will help them stay on task.
Skill #4: Purpose-driven
Central to a teal organization is that everyone is working towards the same goals and driven by the same purpose. As opposed to chasing efficiency and profit, companies that embrace the teal model are looking to change the world.
To run effectively, everyone within the organization needs to be driven and inspired by the same purpose. They need to be drawn to the overall mission instead of a specific title or job role. Employees can then evolve with the company in achieving the purpose together.
Skill #5: Flexibility
Without set roles or hierarchy, teal organizations need a flexible workforce. In this structure, everyone works together to fill any holes in the organization. Those who are more rigid and like to be confined to specific job descriptions may not thrive in that kind of environment.
Skill #6: Responsibility
It’s not an easy task to confront an underperforming peer. However, the group-oriented structure and cooperation mean taking responsibility for the output instead of sticking only to their own work. A teal organization runs on its employees’ ability to take responsibility for themselves and their peers.
An ideal teal worker feels a sense of responsibility for the mission of the organization. They look out for their peers as well as themselves to make sure that everyone succeeds together.
Hiring for a teal organization
As employees become more independent, they want to work at a company with a cause they can get behind and are eager to contribute to every day. Teal organizations use collaboration and purpose, as opposed to a meritocracy or hierarchy, to create structure and work towards a common goal.
Looking to build a teal organization? Our experts can help. Contact us today to see how we can help you find the right candidates using pre-employment testing.
Related posts
Hire the best candidates with TestGorilla
Create pre-employment assessments in minutes to screen candidates, save time, and hire the best talent.
Latest posts
The best advice in pre-employment testing, in your inbox.
No spam. Unsubscribe at any time.

Hire the best. No bias. No stress.
Our screening tests identify the best candidates and make your hiring decisions faster, easier, and bias-free.
Free resources
This checklist covers key features you should look for when choosing a skills testing platform
This resource will help you develop an onboarding checklist for new hires.
How to assess your candidates' attention to detail.
Learn how to get human resources certified through HRCI or SHRM.
Learn how you can improve the level of talent at your company.
Learn how CapitalT reduced hiring bias with online skills assessments.
Learn how to make the resume process more efficient and more effective.
Improve your hiring strategy with these 7 critical recruitment metrics.
Learn how Sukhi decreased time spent reviewing resumes by 83%!
Hire more efficiently with these hacks that 99% of recruiters aren't using.
Make a business case for diversity and inclusion initiatives with this data.